A Guide to WordPress User Roles for Beginners
If you want to run a WordPress website successfully, you must know how to manage user roles effectively.
The larger your site grows, the more you may need additional hands to handle various aspects of its administration, such as content writing, plugin and theme management, eCommerce management, and more.
The last thing you want to do is give everyone full admin access. This is because such an action can cause unintended changes that could be costly enough to lock you out or take your entire site down.
The WordPress user role management function helps you avoid such a costly mistake by letting you control who has access to what on your site.
Using a plugin like ProfilePress gets you access to even more powerful WordPress user roles management features, which are especially useful for membership, multi-author, or community-based sites.
In this guide, we will walk you through the basics of WordPress user roles, covering how they work, how to assign them, their use cases, and how to manage them efficiently.
Let’s jump in!
What Are WordPress User Roles & Capabilities?
A simple analogy for WordPress user roles and capabilities is an office where each team member has a specific role. Everyone is granted access only to the tools they need to do their job.
The password to the company’s safe, for example, will not be given to a marketing intern, as it is sensitive information that they really do not need to perform their job.
Likewise, user roles on a WordPress site are each assigned capabilities that control what a user can access and do on the website. Each role includes only the capabilities most relevant to its execution.
For example, a user assigned the “Editor” role has capabilities limited to content-related tasks such as publishing posts and moderating comments. They will not be able to access settings to manage site plugins or themes.
Approaching WordPress site management this way keeps your site’s files secure by limiting access and also streamlines each user’s workflow to avoid unnecessary distractions.
By default, WordPress allows each user to be assigned only a single role. While this is useful for small websites, it can quickly become limiting as your website grows and you need various users handling multiple responsibilities.
But this isn’t an issue to worry about, as you can easily overcome the limitation, and we will show you how to do so in later parts of this article.
The 6 Default WordPress User Roles Explained
Now, let’s take a look at the six default WordPress user roles that are available and their associated capabilities.
1. Administrator
The highest-authority role in WordPress is the administrator role. This role is automatically assigned to you if you are the owner of a WordPress website and grants total control over all aspects.
Main Capabilities:
- Let you have full access to all WordPress settings so you can tweak site configuration and security options.
- Allows you to install, activate, and delete plugins and themes
- Grants the power to manage all users by creating, editing, and deleting any user account
- Gives you access to all functions for creating, editing, and deleting content
- Enables you to make modifications to core WordPress files and database settings
The only users who should be granted administrator privileges outside the website’s owner are those who are highly trusted. This is important because changes made by admin users can compromise security or break the entire site.
2. Editor
The Editor role was created for users who are responsible for overseeing and managing content publication on a website. This role removes access to technical settings and grants only content-related permissions.
Main Capabilities:
- Enables you to publish, edit, and delete any posts and pages, including those created by other users
- Allows you to manage categories, tags, and other content taxonomies
- Enables you to moderate, approve, and delete comments across the entire site
- Let you upload media files to the WordPress media library and manage them
If you hire an editorial director or chief content officer, for example, that individual can be assigned the Editor user role.
3. Author
When you are assigned the Author role, you can publish your own content, but still have to operate within defined boundaries.
Main Capabilities:
- Allows you to write, edit, and publish your own posts without needing approval
- Let’s you upload media files, such as images, to accompany your content
- Enables you to delete your own published posts whenever necessary
- Allows you to manage the categories and tags that will be used for your own content
Some of the boundaries set for the Author user role include being unable to edit or delete posts created by other users, and access site settings or manage plugins. If you have content writers who need to publish content regularly on your site, you should assign them the Author role.
4. Contributor
The Contributor user role is ideal for content writers who need their work reviewed by an editor before it is published publicly.
Main Capabilities:
- Let’s you write and edit your own posts in draft form
- Enables you to submit posts for review by Editors or Administrators
- Allows you to view published posts but excludes the ability to self-publish
- Let’s you manage your own profile information
Users assigned the Contributor role cannot upload media files, delete posts after submission, or access other users’ content. This role is ideal for guest bloggers, freelance writers, or new team members who are still learning your content standards.
5. Subscriber
The Subscriber user role is the most basic and has the least access to site settings. It is the default role that is assigned to newly registered users on membership or community sites.
Main Capabilities:
- Enables you to log in to the WordPress dashboard with restricted access
- Let’s you view and update your own profile information
- Allows you to read content that may be restricted to registered users only
- Allows you to receive site updates and notifications if configured
Subscribers cannot create, edit, or publish any content. The role is ideal for newsletter subscribers, course participants, or community members who need accounts to access premium content.
6. Super Admin (Multisite Only)
In WordPress Multisite networks, where multiple websites can be run from a single WordPress installation, the Super Admin role has overall administrative control over all sites in the network.
Main Capabilities:
- Let’s you create, delete, and carry out other management tasks on individual sites within the network.
- Allows you to install and manage plugins and themes across all network sites
- Enables you to manage users across the entire network and grants the ability to assign them to different sites
- Let’s you configure network-wide settings that affect all sites in the installation.
The Super Admin role is necessary for managing large-scale WordPress networks, such as university systems, corporate intranets, or website networks operating under a single brand.
The Limitations of Single-User Roles in WordPress
One of the biggest limitations of WordPress’s default user role setting is that you can only assign one role per user. While it works fine for small sites, it can become a headache on larger sites where a single user needs to perform multiple roles.
For example, if you own a membership site that includes a blog and you have a member who is also a contributor to your blog, what role do you assign them?
Ideally, you want them to be both “Contributor” and “Subscriber”. However, with the default user role setting, you can’t have both.
This limitation, over time, leads to workarounds that make user role management complicated and create new problems, such as:
- Granting users higher-level access than necessary
- Giving too little access to where people can’t do their jobs
- Creating multiple custom roles to cover every scenario
- Constantly switching a user’s role based on tasks
In the next section, we’ll look at how this limitation can be addressed by assigning multiple WordPress user roles in a clean, manageable way.
How to Assign User Roles in WordPress (Default Method)
Assigning user roles with the default WordPress settings is pretty simple.
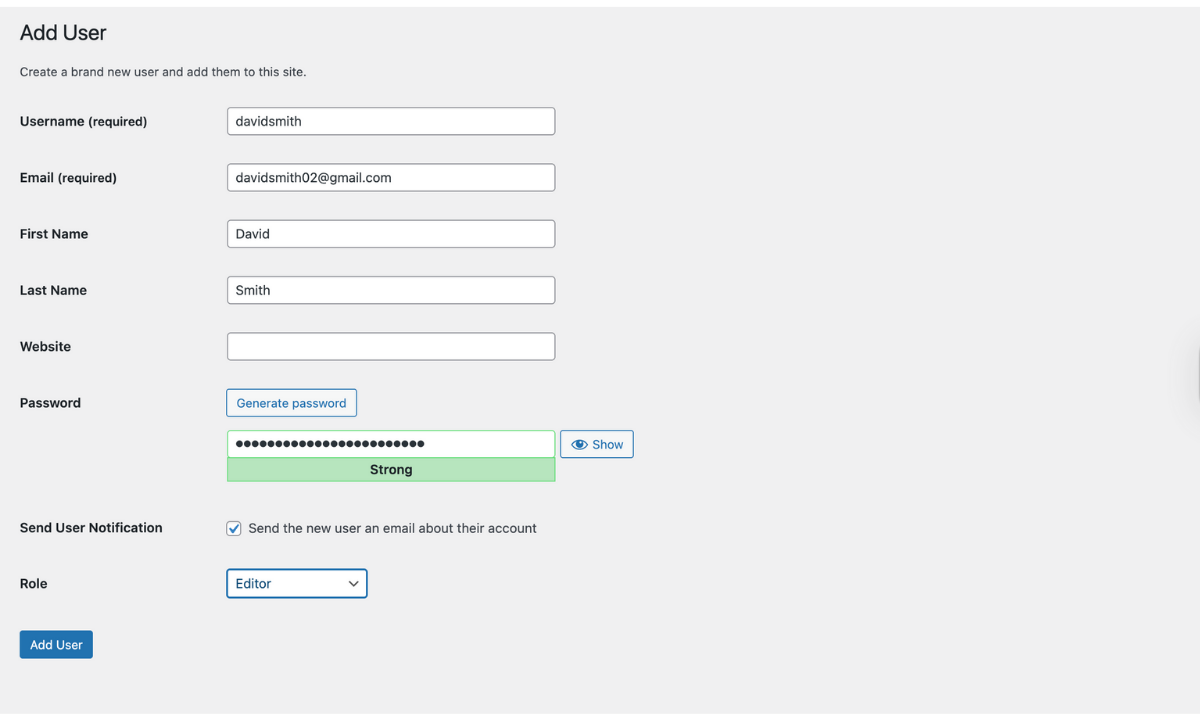
For a new user:
- Go to Users → Add User in your WordPress dashboard
- Fill in the user’s details such as username, email, and password.
- Scroll down to the Role dropdown menu
- Select the appropriate role
- Click Add New User
For existing users:
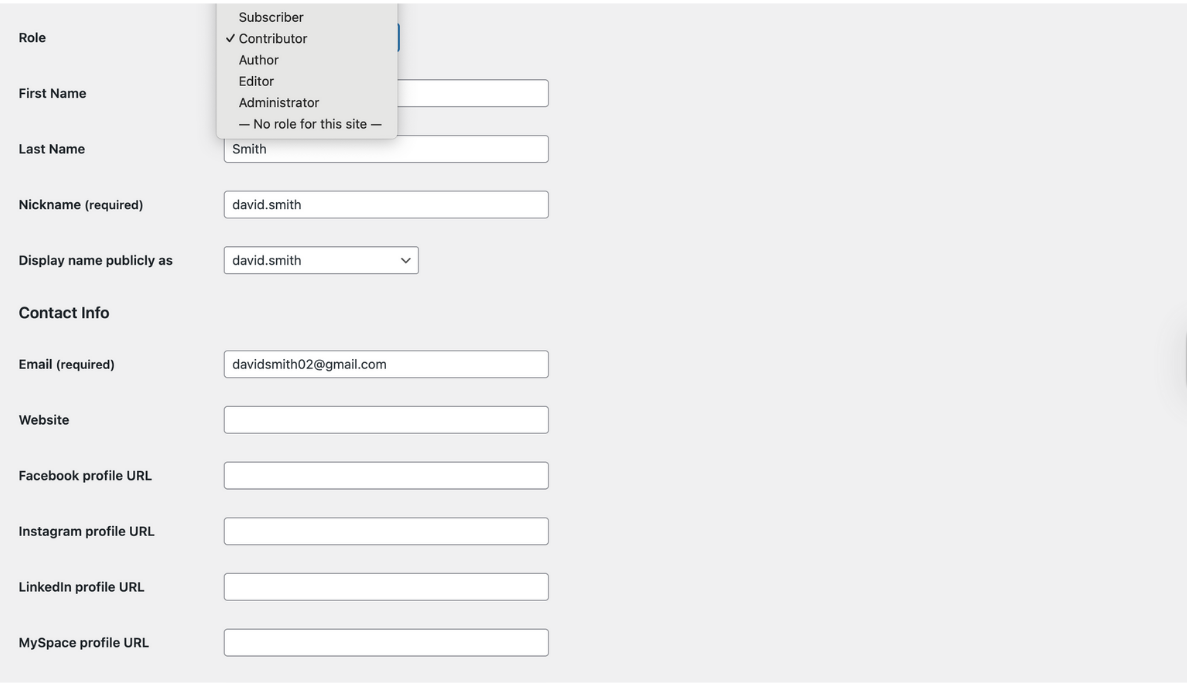
- Navigate to Users → All Users
- Hover over the username and click Edit
- Scroll down to the Role dropdown
- Select the new role
- Click Update User
As you will notice, only one role can be assigned to each user with this default method.
Let’s now explore how to work around this limitation with ProfilePress.
Assigning Multiple WordPress User Roles with ProfilePress
ProfilePress makes it easy to assign multiple WordPress user roles to a single user without writing any custom code or dealing with complex role setups.
It is especially useful for sites where users need access to multiple permission sets to perform their jobs effectively.
Assigning multiple WordPress user roles using the ProfilePress plugin is easy:
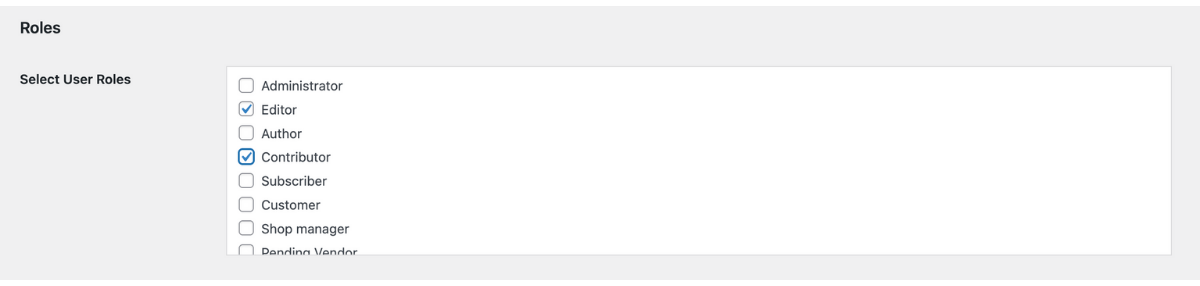
- Install and activate ProfilePress
- Go to Users → All Users in your dashboard
- Click Edit on any user
- Scroll down to find the Roles section, which will now be enhanced by ProfilePress.
- Simply check the boxes for the roles you want to assign to the selected user, e.g., Author AND Customer, Subscriber AND Contributor, etc.
- Click Update User
That’s it. The user will immediately have the combined permissions of those roles.
This approach is valuable for many use cases where assigning multiple roles becomes essential as your WordPress site evolves.
Best Practices for Managing WordPress User Roles
To manage WordPress user roles effectively, there are a few things you need to keep in mind and follow so that things run smoothly:
Follow the principle of least privilege – Only assign users to roles that grant the minimum permission they need to carry out their task as a way to avoid granting unnecessary access to sensitive areas.
Audit your user list regularly – If team members’ responsibilities change or user roles become inactive, take the time to audit and make the necessary updates to maintain security.
Limit Administrator accounts – Try to ensure that you restrict this powerful role to only one or two trusted people. You do not want to have multiple admin users, as it can pose a security risk for your site.
Document your role assignments – Be sure to create clear guidelines that explain when to assign each role, and maintain records of who has what access.
Test before implementing – Always test any changes to a user’s role in a staging environment before applying them to your live site to avoid disruptions.
Conclusion
To choose the right WordPress user role management approach to maintain your site’s security and efficiency, you must understand the various user roles and their capabilities.
Even though the single-user role assignment functionality that comes by default with WordPress works well for simple sites, growing websites that offer memberships often require the flexibility to assign multiple roles to users.
ProfilePress bridges this gap by enhancing WordPress’s default user role management without compromising security.
By implementing proper user role strategies, you’ll protect your site from unauthorized changes while empowering your team to work effectively.
You can always start with WordPress’s built-in roles and then scale your approach as your site’s needs evolve.